ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2001
1. What branch of science study dinosaur fossils?
a) Archaeology
b) Anthropology
c) Paleontology
d) Physics
e) Physical Anthropology
2. When does Patterson assert that western intellectuals coined the term
Acivilization?@
a) 1760s
b) 1890s
c) 1920s
d) 1950s
e) 1990s
3. What is an atlatl?
a) an Aztec dog
b) a device used to throw a spear
c) a type of dwelling in New Mexico
d) a Navajo pit house
e) a ceramic type from the Southwest/Northwest
4. Seriation is
a) a series of typological objects
b) a series of grave markers
c) a temporal ordering of artifacts based on style
d) the layering of deposits in the earth
e) a chronometric dating technique
5. What are plant phytoliths?
a) tiny particles of pollen
b) tiny silica particles contained in plants
c) carbonized fragments of corn
d) plant stems
e) seeds
6. Defacto Refuse:
a) is material deposited as a result of catastrophic abandonment
b) is material that is transported away from the point of use to discard
c) is only found in midden deposits
d) is material discarded at the point of use
e) is material in a trash midden
7. A method of chronometric dating based on the measurement of water absorbtion
on the surface of stone tools:
a) obsidian hydration dating
b) c-14 dating
c) potassium-argon dating
d) amino acid racemization
e) dendrochronology
8. Richard Wetherill is famous for:
a) locating King Tut's tomb
b) identifying the Basketmaker culture
c) developing C-14 dating
d) discovering Troy
e) supporting the Antiquities Act of 1906
9. Howard Carter was successful in finding King Tut=s tomb because
a) he was related to important Egypting government officials
b) he was lucky
c) he worked with a research design
d) villagers led him to the tomb
e) he deciphered the rosetta stone
SHORT ANSWER - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points
each).
10. What is the difference between a random and a hapazord sample?
11. Why did the Dane's begin the archaeological practice of excavating in the ground to learn about the past?
12. Ancient peoples frequently used ceramic vessels. Why do potsherds from these vessels commonly occur on archaeological sites?
13. Why were organic materials preserved at Herculaneum and not at Pompeii?
14. What kind of materials are recovered from archaeological sites using the technique of flotation?
15. List three reasons that living in a cliff dwelling would be beneficial?
16. What are three ways that the Antiquities Act of 1906 protects archaeological sites on federal land in the United States?
17. What is a colonialist archaeology and name two nations of the world that we find such an archaeology today?
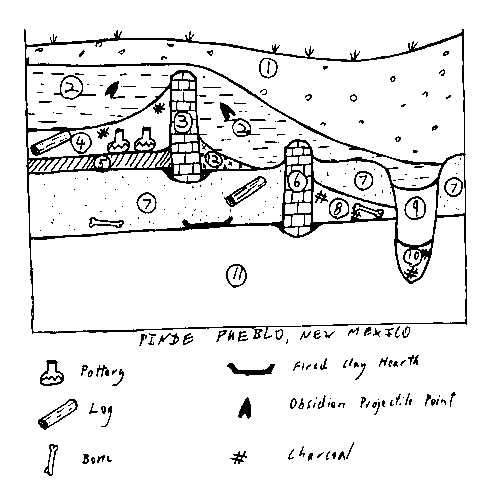
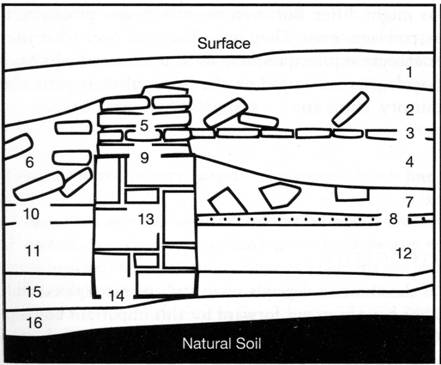
Use the stratigraphic column on the next page to answer the questions that follow it (#s 18-21)
18. List two different dating techniques that could be applied to the profile. For each technique give one stratum (level) you could date with that technique, together with the datable artifact/material. (4 points).
Each of the following is worth 2 points.
19. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship
between strata (levels) 2 and 13.
a. 2 was deposited after 13
b. 2 was deposited before 13
c. 2 and 13 were deposited at the same time
d It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
20.Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between
strata (levels) 7 and 10.
a. 7 was deposited after 10
b. 7 was deposited before 10
c. 7 and 10 were deposited at the same time
d It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
21. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between
strata (levels) 4 and 12.
a. 4 was deposited after 12
b. 4 was deposited before 12
c. 4 and 12 were deposited at the same time
d It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.

Name _______________________________ Section
#_______
Instructions - Answer the multiple choice and short answer questions on
this exam. GOOD LUCK !!!
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
1. Which of these is a relative dating technique?
a. Obsidian Hydration
b. Stratigraphy
c. Dendrochronology
d. Radiocarbon
e. Potassium Argon
2. Which of these is NOT a non-invasive survey technique?
a. Soil resistivity
b. Aerial photography
c. Ground penetrating radar
d. Magnetometry
e. Test pits
3. ____________ was a controversial archaeologist with the reputation
of being a pothunter and a looter who worked in the American Southwest.
a. Heinrich Schliemann
b. Richard Wetherill
c. Randall McGuire
d. Howard Carter
e. Flinders Petre
4. The form of relative dating that is based on the style and likenesses
of artifacts is called: (c)
a. accelerated mass spectrometry.
b. chronometric dating.
c. seriation.
d. halflife.
e. stratigraphy
5. The following is an example of a non-invasive survey technique:
e. Test pits
b. Sondages
c. Ground Penetrating Radar
d. Trenching
e. Soil auger
6. Dendrochronology dating is useful when working on sites that date back
a Tens of years
b Hundreds of years
c. Tens of thousands of years
d. Hundreds of thousands of years
e. To any time.
7. "Inventing Western Civilization" discusses the dominant belief of 16th
Century French Intelligentsia that "life in the present was obviously superior
to life in the past and that change was assumed to be cumulative, directional,
and desirable. Which of the following ideas reflects this view?
a. idea of degeneration
b. idea of regeneration
c. idea of uncivilization
d. idea of progress
e. idea of assembly
8. The whole set of materials an archaeologists wishes to study is called:
a. a feature
b. a sample
c. a population
d. a civilization
e. a neighborhood
9. The distribution of Bison bones found at the Olsen-Chubbuck site in Colorado
is an
example of what kind of archaeological context?
a. Systemic
b. Primary
c. Stratigraphic
d. Post-depositional
e. Secondary
SHORT ANSWER - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points
each).
10. Using the typology of types of archaeology presented in lecture
on "archaeology and the modern world" what type of archaeology is US archaeology
and why?
11. List the four primary factors accounting for the destruction of the
archaeological record.
12. Define use wear and why it is important to archaeological
interpretation?
13. List three characteristics of the ‘stereotypical archaeologist’
that is often portrayed in fiction. Why did Harriet Boyd Hawes not fit
this stereotype?
14. Why did Thomas Jefferson do the first systematic archaeological excavation
in the United States?
15. Why did skeletal remains preserve at Herculenium and not in Pompeii?
What evidence of human remains did preserve in Pompeii and why?
16. What is Systemic context? What is Archaeological context?
17. What are the differences between an additive and reductive technologies
and what are examples of each?
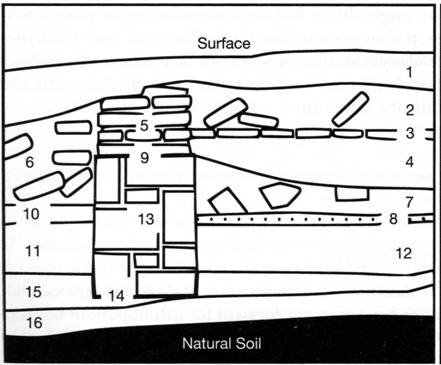
Use the following stratigraphic column to answer the questions that follow
it (#s 18-21)
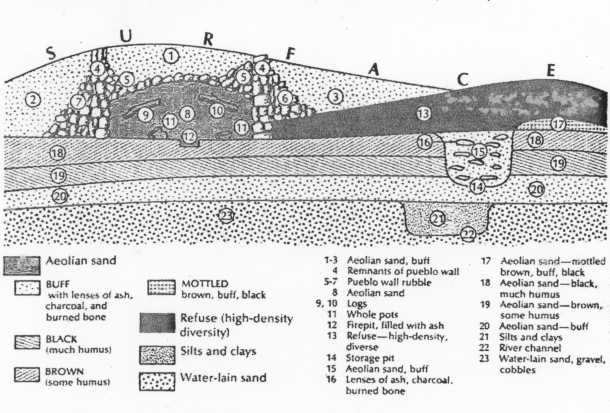
8. List two different dating techniques other than stratigraphy that
could be applied to the profile. For each technique give one stratum
(level) you could date with that technique, together with the datable
artifact/material. (4 points).
Each of the following is worth 2 points.
19. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship
between strata (levels) 8 and 17.
a. 8 was deposited after 17
b. 8 was deposited before 17
c. 8 and 17 were deposited at the same time
d It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
20.Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between
strata (levels) 18 and 14.
a. 18 was deposited after 14
b. 18 was deposited before 14
c. 18 and 14 were deposited at the same time
d It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
21. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between
strata (levels) 16 and 15.
a. 16 was deposited after 15
b. 16 was deposited before 15
c. 16 and 15 were deposited at the same time
d It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2007
Name _______________________________ Section #_______
Instructions - Answer the multiple choice and short answer questions on this exam. GOOD LUCK !!!
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
1. Richard Wetherill’s 1893 excavation at Grand Gulch, Utah is particularly notable for:
A. the earliest evidence of paleo-Indian warfare
B. the first Native American remains to be repatriated under NAGPRA
C. the first use of stratigraphy in US archaeology to define Basketmaker
D. the first use of luminescence dating
E. the exposure of the Hohokam period as a scientific hoax
2. Which of the following is an example of relative dating?
A. Thermoluminescence
B. Radiocarbon
C. Dendrochronology
D. Obsidian hydration
E. Seriation
3. The enactment of Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act of 1990
A. protected archaeologists from angry Native Americans
B. protected museum collections from repatriation
C. repatriated human remains and artifacts to the Bureau of Indian Affairs
D. did not impact archaeology
E. repatriated human remains and artifacts to Native Americans
4. Ecofacts are:
A. natural remains that have cultural significance
B. objects manufactured by people
C. facts about the environment
D. theories pertaining to the environment
E. non-portable
5. Which ONE of the following is a feature of the Archaeological Resource Protection Act of 1979?
A. it is the first federal law to make digging of archaeological sites without a permit, illegal
B. made archaeological sites eligible to be listed in the National Register of Historic Places
C. makes pothunting on federal land a felony
D. empowered National Park Service to identify and document historic and archaeological sites
E. the US President can reserve federal land as national monument
6. King Priam’s treasure from Troy is currently located in __________.
A. Britain
B. Turkey
C. Germany
D. Greece
E. Russia
7. Paleofeces can yield information about:
A. National heritage
B. Gender roles
C. Health and diet
D. Family size
E. Trade and exchange
8. Janet Spector’s feminist archaeology of the Dakota in Minnesota is an example of which theoretical approach?
A. culture history
B. processual
C. postprocessual
D. nationalist
E. evolutionary
9. The Piltdown Man was:
A. discovered to be a hoax through the scientific method
B. a famous Neanderthal skull found in Java
C. used to support Aryan race theory and Nazi nationalism
D. found to be the “missing link”
E. reconstructed at Pompeii by filling hollows inside ash with plaster
10. What did the UNESCO Convention of 1970 and the Unidroit Convention of 1995 both advocate?
A. the expansion of nationalist archaeology
B. the protection of private collections of antiquities
C. the return of stolen antiquities to their countries of origin
D. the protection of the archaeological record from economic development
E. the extension of NAGPRA to international museums
SHORT ANSWER - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
11. Why did archaeologists in the first half of the 20th century ignore Harriet Boyd Hawes and give credit for her work at Gournia in Crete, to her photographer?
12. What is the difference between an archaeological feature and an artifact? Give an example of each.
13. Which chronometric (absolute) dating method discussed in lecture, readings and sections has the potential to be the most precise, and why?
14. List the four major factors that threaten archaeological sites today?
15. What are four things that bioarchaeologists can tell us about ancient peoples from their skeletons?
16. What are two contrasts between archaeology and pothunting?
17. What is Indigenous Archaeology?
18. Your beloved dog Buster has just died and you decide to mummify him“Egyptian style” so that he may have eternal life. List 4 things you would have to do to Buster in order to successfully mummify him.
19. Scientific archaeology accepts the stratigraphic principle of uniformitarianism. Define uniformitarianism.
20. Nazi archaeology is an example of what kind of archaeology? List three reasons some German archaeologists supported Nazi archaeology?
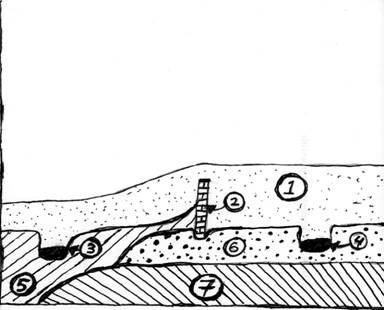
Use the stratigraphic column below to answer the questions that follow it (#s 21-24) 2 points each
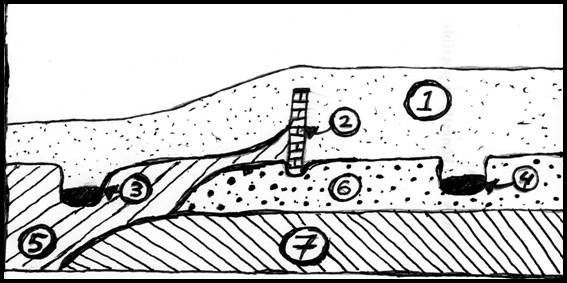
21. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between Stratum 5 and Stratum 6 in the profile?
A. 5 was deposited before 6
B. 6 was deposited before 5
C. 5 & 6 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
22. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 3 (a pit) and 4 (a pit) in the profile?
A. 3 was deposited before 4
B. 4 was deposited before 3
C. 3 & 4 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
23. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 2 (the wall) and Strata 6 in the profile?
A. 2 was deposited before 6
B. 6 was deposited before 2
C. 2 & 6 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
24. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 2 (the wall) and 4 (the pit on the right) in the profile?
A. 2 was deposited before 4
B. 4 was deposited before 2
C. 2 & 4 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2009
Name ____________________________________________ Section #_______
Instructions - Answer the multiple choice and short answer questions on this exam. GOOD LUCK !!!
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
1. Which of the following is an example of a feature?
2. Richard Wetherhill’s excavations and homestead at Chaco Canyon led to Congress passing which act?
3. In his book Leviathan ________________ portrayed the natural state of humanity as one of perpetual conflict which could only be stemmed by the ceding of individual power to a sovereign?
4. Which ancient city, consisting of roughly a hundred mounds is located just east of the modern city of St. Louis, Missouri?
5. Which archaeological technique has been instrumental in the recovery of floral and micro-faunal remains from archaeological sites?
6. What is meant by provenience?
a. The color of an artifact
b. Finding an artifact underwater
c. The shape of an artifact
d. The precise three dimensional coordinates of an artifact
e. Recording the composition of an artifact
7. Who sponsored the excavations conducted by Howard Carter in Egypt?
a. His wife, Sophia
b. Dr. V. Gordon Childe
c. Lord Carnarvon
d. Mr. Charles Lyell
e. Richard Wetherill
8. Where did Heinrich Schliemann “discover” the ancient city of Troy?
a. Zhanxia in eastern China
b. Central Arkansas
c. Hissarlik in western Turkey
d. Mont Blanc, France
e. Masada, Israel
9. According to “Patterns in Prehistory,” which of the following methods can be used to date rock and volcanic ash?
10. Which of the following best describes defacto refuse?
SHORT ANSWER - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
11. What is the difference between random sampling and haphazard sampling?
12. Define artifacts and ecofacts and give an example of each.
13. How and why did preservation differ at Pompeii and Herculaneum?
14. List the four major factors that threaten archaeological sites today?
15. Define a Nationalist approach to archaeology and give an example.
16. What are the four subfields of American Anthropology?
17. Define the concept of primary context. Why are primary contexts important archaeologically?
18. Your beloved dog Buster has just died and you decide to mummify him“Egyptian style” so that he may have eternal life. List 4 things you would have to do to Buster in order to successfully mummify him.
19. What are the two types of Remote Sensing methods? Provide an example of each.
20. Define additive and reductive technologies and give an example of each
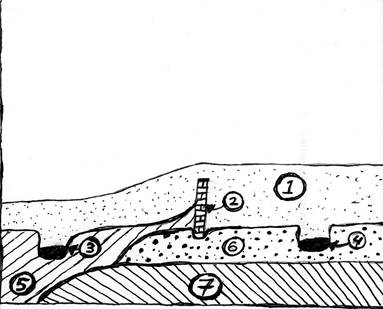
Use the stratigraphic column below to answer the questions that follow it (#s 21-24) 2 points each
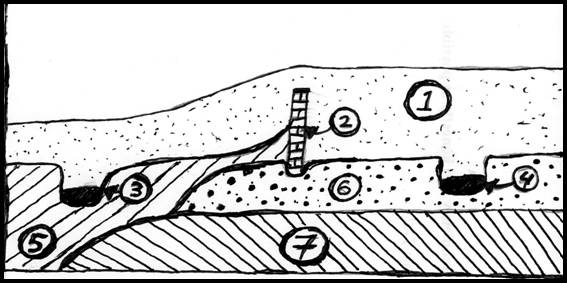
21. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between Stratum 1and Stratum 5 in the profile?
A. 5 was deposited before 1
B. 1 was deposited before 5
C. 5 & 1 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
22. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 3 (a pit) and 4 (a pit) in the profile?
A. 3 was deposited before 4
B. 4 was deposited before 3
C. 3 & 4 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
23. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 2 (the wall) and Strata 6 in the profile?
A. 2 was deposited before 6
B. 6 was deposited before 2
C. 2 & 6 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
24. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 2 (the wall) and 3 (the pit on the right) in the profile?
A. 2 was deposited before 3
B.3 was deposited before 2
C. 2 & 3 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2010
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
2. What is taphonomy?
3. Which of the following is an example of an A-S (reclamation) process?
4. In the movie “ Thieves of Time” which of the following images was NOT shown (hidden)?
5. In the nineteenth century what were two theories for how the earth was formed?
6. The Parthenon or Elgin Marbles reside in the _______ museum.
7. Unprovenanced artifacts lack
8. Who was given the nickname “Anasazi” by the Navajo?
9. ”Natural remains that have cultural significance” are called:
Short Answer - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
11. Gamble in Archaeology The Basics loosely divides archeological approaches into two categories. Name these and give one example of each.
12. Define antiquarianism.
13. List the four processes that destroy the archaeological record (sites)?
14. Why were organic materials preserved at Herculaneum but not at Pompeii?
15. In Archaeology the Basics, Gamble lists three political traditions of archaeology. List two of these and give an example of each?
16. What are two reasons that ‘First Americans’ have objected to what archaeologists do?
17. What is Cultural Resource Management (CRM)?
18. List two reasons why people would choose to live in cliff dwellings.
19. What is the dialectical relationship between human action and material patterns?
20. List two reasons that King Tut’s tomb was not looted and survived intact until the 20th century?
Use the stratigraphic column below to answer the questions that follow it (#s 21-24) 2 points each
21. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between Stratum 1and Stratum 5 in the profile?
A. 5 was deposited before 1
B. 1 was deposited before 5
C. 5 & 1 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
22. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 11 and 12 in the profile?
A.11was deposited before 12
B.12 was deposited before 11
C.11 & 12 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
23. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 2 and Strata 8 in the profile?
A. 2 was deposited before 8
B. 8 was deposited before 2
C. 2 & 8 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
24. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 9 and 15 in the profile?
A. 9 was deposited before 15
B.15 was deposited before 9
C. 9 & 15 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
ANTHROPOLOGY
First Exam - Spring 2011
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
James Deetz’s study of the Colonial Gravestones in Massachusetts is a good example of the use of what technique?
Which law made it necessary to have a permit to excavate on federal land?
a. Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act of 1990
b. Antiquities Act of 1906
c. National Historic Preservation Act of 1966
d. Federal Research Act of 1900
e. Archaeological Regulation Act of 1915
3. Radiocarbon dating would be best used on:
4. Archaeologists can use pollen to reconstruct?
5. Which of these statements best describes the process of Systematic Sampling?
a) Relies on prior knowledge or past work experiences
b) A patterned method is used to choose sample units
c) Each unit has an equal chance of being in the sample
d) No formal method is used to select sample units
e) Every possible unit is selected
6. The study of the relationship between humans, their cultures and their environment is called what?
a. ethnographic analysis
b. physical anthropology
c. cultural ecology
d. bio-anthropology
e. GIS
7. The Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation ACT of 1990 (NAGPRA) does what?
8. . In Linking to the Past by Feder, what state did he do his excavations?
a. Arizona
b. New Mexico
c. Connecticut
d. Massachusetts
e. New York
9. An appreciation for old objects as things, not as sources of knowledge about the past, is defined as:
a) Uniformitarianism
b) Antiquarianism
c) Archaeology
d) Nationalism
e) Rationalism
Short Answer - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
11. What is the difference between relative and chronometric dating methods?
12. What formation processes enabled archaeologists to create the plaster casts of bodies at Pompeii? Why is it not possible to create plaster casts of bodies at Herculaneum?
13. List two reasons that Richard Wetherill is an important figure in the history of archaeology in the
United States.
14. . In Linking to the Past, Feder argues that archaeology is like detective work. List two of the ways
that archaeologists are like detectives.
15. Based on both your readings and the film “Thieves of Time,” list two reasons why Native
Americans might object to the work that archaeologists do.
16. What are two of the steps in Howard Carter’s research design to search for King Tut’s tomb?
17. Which contemporary process is most destructive of the archaeological record?
18. Give two examples of A-S (deposition) cultural formation processes.
19. List two activities that archaeological reconstructions typically portray women performing.
20. List two processes for forming ceramic vessels.
Use the stratigraphic column below to answer the questions that follow it (#s 21-24) 2 points each
21. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between Stratum 2 and Stratum 12 in the profile?
A. 2 was deposited before 12
B. 12 was deposited before 2
C. 2 & 12 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
22. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 10 and 8 in the profile?
A.10 was deposited before 8
B.8 was deposited before 10
C.10 & 8 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
23. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 6 and Strata 15 in the profile?
A. 6 was deposited before 15
B. 15 was deposited before 6
C. 5 & 15 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
24. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 5 and 15 in the profile?
A. 5 was deposited before 15
B.15 was deposited before 5
C. 5 & 15 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2012
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
In his book Linking to the Past Kenneth Feder uses the site of __________ as his main case study.
Howard Carter found King Tut’s tomb
Short Answer - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
11. List four chronometric dating techniques that archaeologists commonly use?
12. What are two reasons that burials are important in the analysis of equality and inequality in archaeological record of an ancient group of people?
13. Bio-archaeologists study human skeletons to learn about people’s lives in the past. What are two things that they can learn about ancient lives and what features of the skeleton do they use to identify each?
14. How is lithic production a reductive technology?
15. Based on both your readings and the film “Thieves of Time,” list two reasons why Native
Americans might object to the work that archaeologists do.
16. What are the four major cultural processes that threaten archaeological sites?
17. Why is a haphazard sample never a good approach to collecting information?
18. Give two examples of A-A (disturbance) cultural formation processes.
19. List three reasons that people lived in Cliff Dwellings in the Southwest/Northwest.
20. Name two types of climates in which you will most likely find organic archaeological materials preserved and the corresponding geographical locations where these occur.
Use the stratigraphic column below to answer the questions that follow it (#s 21-24) 2 points each
21. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between Stratum 2 and Stratum 7 in the profile?
A. 2 was deposited before 7
B. 7 was deposited before 2
C. 7 & 12 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
22. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 3 and 4 in the profile?
A.3 was deposited before 4
B.4 was deposited before 3
C.4 & 3 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
23. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 6 and Strata 5 in the profile?
A. 6 was deposited before 5
B. 5 was deposited before 6
C. 6 & 5 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
24. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 5 and 2 in the profile?
A. 5 was deposited before 2
B. 2 was deposited before 5
C. 5 & 2 were deposited at the same time
D. It is impossible to tell from the profile
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2013
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
2. A future archaeologist uncovers a lecture hall full of dead students with their cell phones. In order to date this disaster, he calculates the percentage of flip phones, Blackberry phones, and smart phones and checks them against a charted “battleship curve” of flip phone, Blackberry, and smart phone popularity. What is the name of this technique?
9. Radiocarbon dating would not be used to date the death of a recent murder victim for the following reason:
Short Answer - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
12. List four primary types of actions accounting for the destruction of the archaeological record?
13. Name two reasons why dendrochronology cannot be used in some areas.
14. What is the difference between an additive technology such as ceramics and a reductive technology such as lithic artifact production?
15. What can archaeologists learn from phytoliths?
16. Why were organic remains preserved in Herculaneum and not in Pompeii?
17. Define the law of superposition, a principle on which stratigraphic excavation is based.
18. List two steps in the research design that Howard Carter used to find King Tut’s tomb.
19. What role did Richard Wetherill play in the formulation and passage of the Antiquities Act of 1906?
20. Name two ways that Schliemann’s excavations at Troy inspired the stereotype of the movie archaeologist.
Use the stratigraphic column below to answer the questions that follow it (#s 21-24) 2 points
21. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between Stratum 2 and Stratum 1 in the profile?
22. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 3 and 6 in the profile?
23. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 6 and Strata 2 in the profile?
24. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between 1 and 7 in the profile?
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2014
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
2. Pompeii represents an example of what refuse type of cultural formation processes?
Short Answer - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
14. List two of the three reasons that living in a cliff dwelling would be beneficial in the Southwest/Northwest:
16. Why are there no plaster casts of bodies at Herculaneum?
19. What is the source of bias in (1) a systematic sample and (2) a judgmental sample?
20. Ancient Egyptians attempted to erase the history of the Great Heresy. What are two things they did to specifically obliterate the history of King Tutankhamen?
21. List the four primary factors accounting for the destruction of the archaeological record:
22. Why was Harriet Boyd Hawes not given credit for her archaeological work in Gournia, Crete?
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2015
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
1. A sampling strategy based upon prior knowledge is called a:
Short Answer - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
11. What is the difference between a random and a haphazard sample? Please give an example of each.
12. What is the difference between an additive and a reductive technology? Please give an example of each.
16. What is the difference between relative and chronometric (absolute) dating? Please give an example of each.
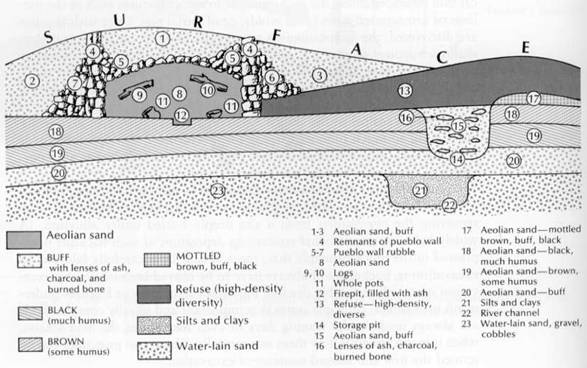
Each of the following is worth 2 points.
21. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between strata (levels) 8 and 16?
a. 8 was deposited after 16
b. 8 was deposited before 16
c. 8 and 16 were deposited at the same time
d. It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
22. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between strata (levels) 18 and 23?
a. 18 was deposited after 23
b. 18 was deposited before 23
c. 18 and 23 were deposited at the same time
d. It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
23. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between strata (levels) 3 and 15?
a. 3 was deposited after 15
b. 3 was deposited before 15
c. 3 and 15 were deposited at the same time
d. It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
24. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between strata (levels) 13 and 19?
a. 13 was deposited after 19
b. 13 was deposited before 19
c. 13 and 19 were deposited at the same time
d. It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2016
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
1. Where are the most jobs for archaeology coming from in the United States today?
a) museums
b) antique shops
c) private firms
d) academia (universities)
e) National and State Park Systems
2. Which would be an example of experimental archaeology?
a) pH testing soil samples in a lab
b) reconstructing how the stones of Stonehenge may have been moved by erecting a 50 ton block of concrete
c) imagining what types of emotions people in the past may have felt
d) excavating a Neolithic village
e) comparing artifacts from many different sites and sorting them into style-types
3. According to your text, which chronometric dating method is best used on igneous rocks?
a) K/Ar dating
b) C-14 dating
c) seriation
d) dendrochronology
e) stratigraphy
4. Percussion flakes, pressure flakes, and striking platforms are all terms related to___________________________.
a) ancient military bases
b) pottery manufacture
c) grinding grain
d) flintknapping
e) fish weirs
5. Which of the following is a relative dating technique?
a) dendrochronology
b) frequency seriation
c) potassium argon dating
d) laser ablation
e) paleomagnetic dating
6. One of Richard Wetherill’s enduring legacies was________________________________________________.
a) the professionalization of archaeological practice in the U.S.
b) a better understanding of the mound builder controversy
c) the development of the three age system
d) the fact that he got to keep his homestead in Chaco Canyon
e) the excavation of Troy
7. Why are modern archaeologists somewhat critical of the excavations conducted at Herculaneum and Pompeii in the 18th century?
a) The lack of frescoes in Pompeii could be attributed to them.
b) They left no artifacts behind for later excavators to find.
c) The felt that the use of heavy equipment was an inappropriate excavation technique.
d) They put fig leaves on all the phallic symbols.
e) Early excavators were not concerned with the context of items they found.
8. King Tutankhamen____________________________________________________________.
a) is regarded as one of the most influential kings of Egyptian history
b) was sold and used to make paper in England
c) was buried in his jammies
d) is far more influential today than he was in life
e) was buried with a number of sacrificed attendants
9. What dangers do archaeologists commonly face?
a) curses
b) poison ivy
c) flowing lava
d) mummy attacks
e) Nazis
10. What does an Antiquarian want?
a) knowledge
b) power
c) old things
d) artifacts in their 3-D context
e) mystical powers
Short Answer - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
11. Why was archaeology an important tool of nationalism in Denmark (and Scandinavia more generally)?
12. List two reasons that archaeologists interpret the Egyptian pyramids and Mesoamerican pyramids as independent inventions rather than as an example of diffusion.
13. What is the difference between an “ecofact” and an “artifact”? Provide an example of each.
14. Our lecture hall has been covered in a freak landslide and no one excavates it for 500 years. Name two objects that would be preserved, and two that would not be preserved in this archaeological record.
15. List two provisions of the Antiquities Act of 1906.
16. What is one way in which Harriet Boyd Hawes’s role in Bronze Age archaeology was similar to that of Sophia Schliemann and what is one way in which it was different?
17. Why would it not be a good thing to excavate all existing archaeological sites RIGHT NOW, even if we had the resources and person power required to do such a thing? List TWO reasons why it is beneficial to save some sites
18. What are two reasons why living in a cliff dwelling would be beneficial? What are two reasons why living in a cliff dwelling would be problematic?
19. What are two different methods of making a ceramic vessel? Is ceramic production an additive or reductive form of technology?
20. According to Feder, what is one consequence that results from the sponsorship of archaeological projects by wealthy patrons?
21. Much of archaeology has focused on culture history. What are two traits of a cultural historical approach?
22. List four tools that archaeologists use during excavation to expose and recover artifacts.
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2017
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
Short Answer - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
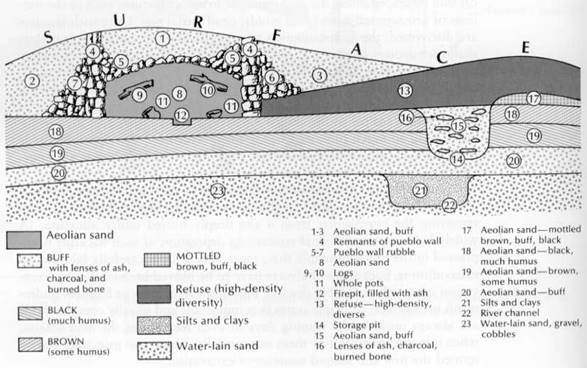
Each of the following is worth 2 points.
21. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between strata (levels) 8 and 15?
a. 8 was deposited after 15
b. 8 was deposited before 15
c. 8 and 15 were deposited at the same time
d. It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
22. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between strata (levels) 18 and 20?
a. 18 was deposited after 20
b. 18 was deposited before 20
c. 18 and 20 were deposited at the same time
d. It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
23. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between strata (levels) 3 and 19?
a. 3 was deposited after 19
b. 3 was deposited before 19
c. 3 and 19 were deposited at the same time
d. It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
24. Which of the following describes the chronological relationship between strata (levels) 3 and 13?
a. 3 was deposited after 13
b. 3 was deposited before 13
c. 3 and 13 were deposited at the same time
d. It is not possible to determine the relationship of these strata.
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2018
Name _____________________________________________ Section #_______
Instructions - Answer the multiple choice and short answer questions on this exam. GOOD LUCK!!!
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
1. The Antiquities Act of 1906 empowers __________ to declare federal lands as national monuments?
a. The people who live there
b. The President of the United States
c. The Archaeologist who excavated it
d. Congress
e. The Governor of a state
2. Who funded Howard Carter’s excavations in Egypt?
a. Richard Wetherill
b. Lord Carnarvon
c. George Pepper
d. T.M. Prudden
e. The Hyde Brothers
3. Some of the earliest and most important archaeology on the island of Crete was conducted by:
a. Heinrich Schliemann
b. Marietta Wetherill
c. Harriet Boyd Hawes
d. Kenneth Feder
e. Howard Carter
4. Based on Feder’s book Linking the Past, what method helps us to reconstruct ancient environments by examining tree rings?
a. Environmental approach
b. Empiricism
c. Geographical Information System
d. Dendrochronology
e. Radiocarbon analysis
5. According to Olzewski and Wenke (Patterns in Prehistory), which artifact class is not suitable for seriation?
a. pottery
b. Chevrolets
c. stone tools
d. decorated objects
e. gravestones
6. In the spoof of archaeology, Motel of Mysteries, the archaeologist’s wife wore a toilet seat around her neck. Which archaeological method could they have used to figure out what the real use of a toilet seat is?
a. seriation
b. GIS
c. lithic analysis
d. LIDAR
e. use wear
7. Early European archaeologists studied living primitive peoples to
a. help define Nation States
b. understand prehistoric peoples in Europe
c. to build collaborative projects with the locals
d. enhance colonial power relations
e. discover local knowledge that could be used by Europeans
8. Why were wooden items preserved in Herculaneum?
a. Herculaneum was located in a region with dry and stable climate
b. The remains were frozen
c. The wooden items were carbonized due to the high temperatures of pyroclastic flow
d. The wooden items were buried under piles of ash
e. Wood is a material with excellent preservation
9. Archaeologists use the flotation technique to
a. recover soil sample.
b. test which artifacts can float
c. recover floral and micro-faunal remains
d. wash artifacts
e. test which artifacts can sink
10. In archaeology, who is a shovel bum?
a. A university professor
b. A construction worker
c. A field technician
d. A neighbor who keeps borrowing shovels
e. A pothunter
SHORT ANSWER - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
11. List the four factors that determine the decisions and compromises made for excavation of an archaeological site.
12. When digging archaeological sites, why must archaeologists record artifacts and features in 3 dimensional space?
13. Define Antiquarianism.
14. What is the dialectical relationship between human action and material patterns?
15. According to Wenke and Olzewski (Patterns in Prehistory), what are two types of evidence of that archaeologists can use to reconstruct ancient environments?
16. List four reasons why people are fascinated with the archaeological site of Pompeii.
17. There are four ways in which cultural formation processes create archaeological contexts. Identify 2 of them and give an example for each.
18. List the four primary factors that account for archaeological site destruction.
19. Define what is an archaeological research design and list the three parts of an archaeological research design.
20. What is the difference between primary and secondary refuse? Give examples of each.
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2020
Multiple Choice - Circle the correct answer - (2 points each)
What was the first step in Howard Carter’s research design?
The branch of archaeology concerned with studying living or recent peoples to better understand the archaeological record is called:
Which one of the following dating methods is associated with Wetherill’s excavations?
SHORT ANSWER - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2022
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
SHORT ANSWER - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
11. What is a research design? List the 3 steps involved in research design:
12. What are two kinds of evidence that archaeologists use to reconstruct ancient diets?
13. List four “signs” of a crackpot.
14. If you were to perform use-wear analysis on a projectile point, how could you discriminate between natural weathering as opposed to wear from its use by humans?
15. What is the difference between archaeology and paleontology?
16. How did Roman roof tiles end up in lower Manhattan in the 1940s?
17. How does Bahn (the small book) define cognitive archaeology?
18. What is one way that the character Laura Croft reinforces popular stereotypes of archaeologists and one way that she differs from these stereotypes?
19. What are the four major factors that account for the destruction of archaeological sites?
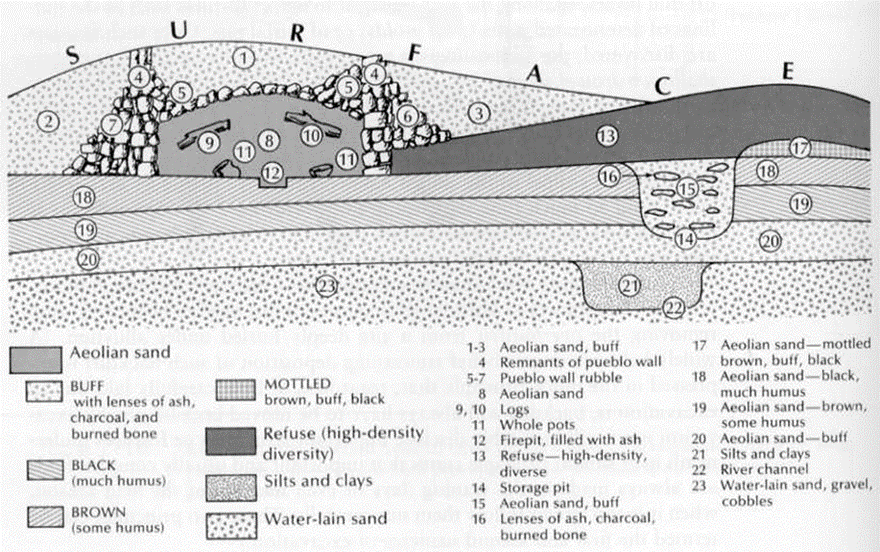
Each of the following is worth 2 points.
ANTHROPOLOGY 125
First Exam - Spring 2023
Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer - (2 points each)
Who is credited with locating/excavating King Tut’s tomb?
According to Bahn, “Archaeology of the mind” that studies the minds and thoughts of past peoples or prehistoric mindways is also called:
Small scale societies of hunters, gatherers, and fishers, usually numbering less than 100 people who usually moved around with the seasons:
The 12th century Angkor Wat is a Hindu temple and the largest religious monument in the world. It is located in:
Ostia Antica of ancient Rome served as:
What technique did Wetherill introduce to southwest archaeological practice?
What comes first in archaeological research?
How might the great stone heads (Moai) of Rapa Nui been moved?
) What about Stonehenge is frequently cited by crackpot theorists as a reason that humans could not have built the monument?
SHORT ANSWER - You do not need to answer in complete sentences (4 points each).
11. What are two distinctive methodological elements that distinguish archaeology from antiquarianism?
12. How do Bahn and Fagan explain the preservation of bog bodies?
13. How do US fderal laws protecting archaeological heritage differ from similar laws in most of the world?
.14. List two ways Looting is so detrimental to the archaeological record.
15 What are two similarities and two differences between the archaeological sites at Pompeii and Herculaneum?
16. List the 4 fields of Anthropology?
17. What is the difference between random and haphazard sampling? Which one should you never use?
18. List four technologies (toys) that aid archaeologists in surveying, mapping and analysis?
19. What are two provisions of the Antiquities Act of 1906?
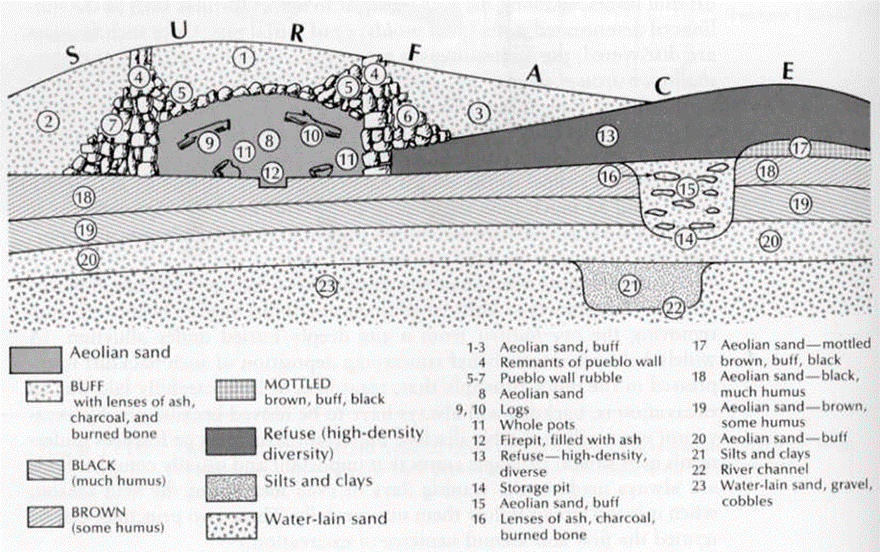
Each of the following is worth 2 points.